1.线程间通讯的理解
线程间通讯:
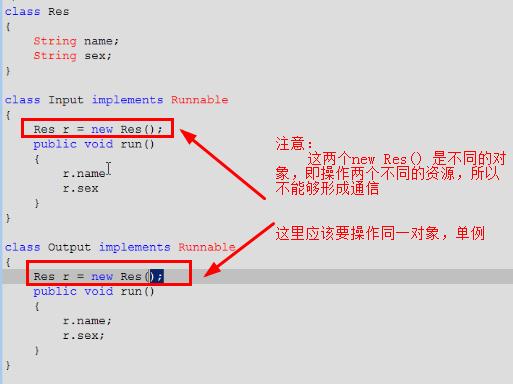
其实就是多个线程在操作同一个资源,但是操作的动作不同
2.线程间通信的示例代码
描述:存在两个线程,一个线程负责写入信息,另一个线程负责打印信息。
model类Student 属性name sex (私有类) 线程:Input类,Output类。启动两个线程分别执行打印和写入操作。
/** * */ package threadCommnication; /** *Title: InputOutputDemo
*Description:
*Company:
* @author 夏 杰 * @date 2015年12月12日 下午8:40:53 * @vesion 1.0 */ public class InputOutputDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Student student = new Student(); Input input = new Input(student); Output output = new Output(student); //存入学生信息的线程 new Thread(input).start(); //打印学生信息的线程 new Thread(output).start(); } }
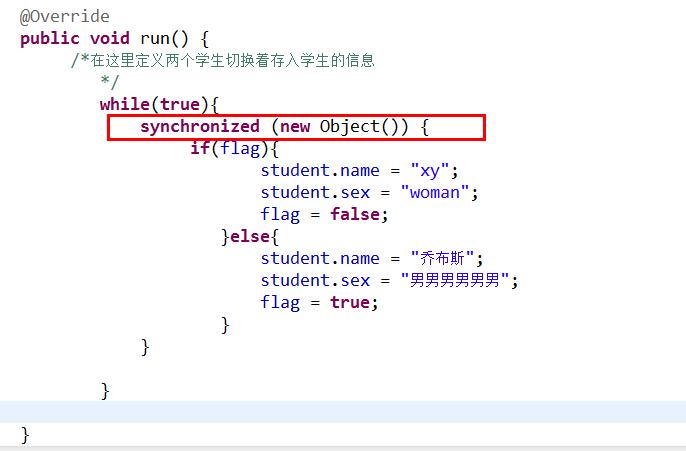
/** * */ package threadCommnication; public class Input implements Runnable{ private Student student; boolean flag = false; //保证传入对象唯一性 public Input(Student student) { this.student = student; } @Override public void run() { /*在这里定义两个学生切换着存入学生的信息 */ while(true){ if(flag){ student.name = "xy"; student.sex = "woman"; flag = false; }else{ student.name = "乔布斯"; student.sex = "男男男男男男"; flag = true; } } } } /** * */ package threadCommnication; public class Output implements Runnable{ private Student stu; public Output(Student stu){ //保证传入对象唯一性 this.stu = stu; } @Override public void run() { while(true){ System.out.println(stu.name+"..."+stu.sex); } } } public class Student { String name; String sex; }
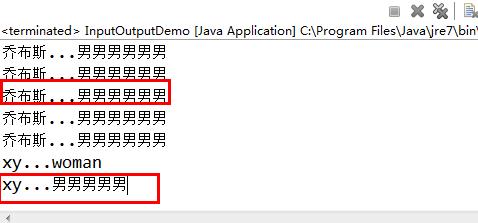
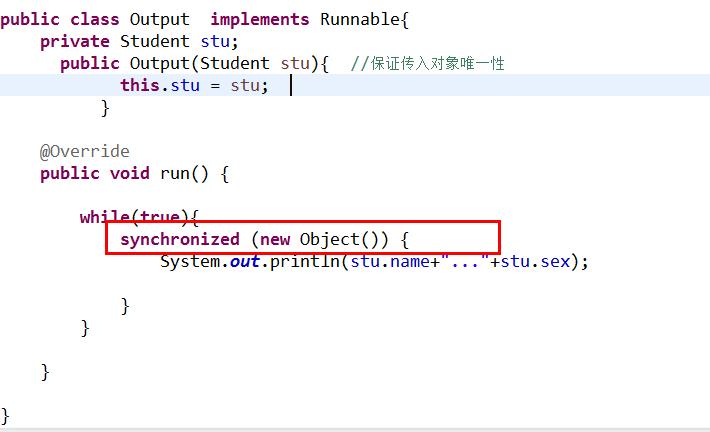
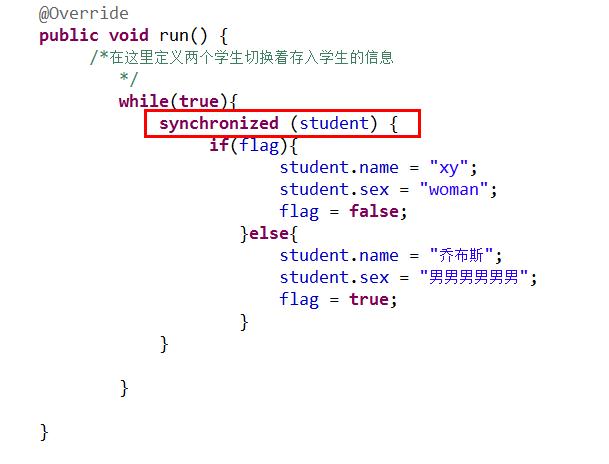
但是虽然加了同步锁,但是由于加的锁并不是同一个把锁,所以不能够限制对象同步,还会出现不同步的情况
这是就需要检查同步的前提条件了:
同步的前提: 1、至少有两个线程,在程序中运行 2、同步时使用同一个锁对象
注意:最好不要在整个方法上加锁,最好在代码块上,因为一个方法上不可能全部都是互斥的,这样执行效率会比较低
改成这样就行了,同用student这把锁
3.多线程中的唤醒等待机制(重要)
Object类中存在以下方法:
wait(): notify(); notifyAll();特点:都使用在同步当中,因为要对持有锁(监视器)的对象操作。
所以要在同步中使用,因为同步中才有锁。描述:要求input类读入一个信息,紧接着output就打印出这条信息。
解决思路: 我们需要将这个类添加一个标识flag。 flag==flase时:表示input没有信息 input开始读入信息,将flag设置为true,并将output唤醒 flag==true时:表示input有信息。 ouput开始打印信息,将flag设置为false,并唤醒inputpublic class InputOutputDemo1{ public static void main(String args[]){ Student stu = new Student(); Input in = new Input(stu); Output out = new Output(stu); Thread t1 = new Thread(in); //存入学生信息的线程 Thread t2 = new Thread(out); //打印学生信息的线程 t1.start(); t2.start(); } } class Input implements Runnable{ private Student stu; boolean flag = false; int x=0; public Input(Student stu){ this.stu = stu; } public void run(){//这个线程的run方法负责将姓名和性别存入 /*在这里定义两个学生切换着存入学生的信息 */ while(true){ if(flag){ stu.set("xy","woman"); flag = false; }else{ stu.set("李志磊","男男男男男"); flag = true; } } } } class Output implements Runnable{ private Student stu; public Output(Student stu){ //保证传入对象唯一性 this.stu = stu; } public void run(){ while(true){ stu.out(); } } } class Student{ private String name; private String sex; private boolean flag; //设置标志,默认为false public synchronized void set(String name,String sex){ if(flag) try{this.wait();}catch(Exception e){}; this.name = name; this.sex = sex; flag = true; this.notify(); } public synchronized void out(){ if(!flag){ try{this.wait();}catch(Exception e){}; }else{ System.out.println(name+"-----"+sex); flag = false; this.notify(); } } }